Skin tags are a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. They are small, soft, benign growths that typically appear on areas of the body where skin folds or experiences friction. While most skin tags are harmless, many people wonder about their potential to spread. This article will answer the question: Are Skin Tags Contagious? We’ll explore the causes, risk factors, treatment options, and ways to maintain overall skin health.
What Are Skin Tags?
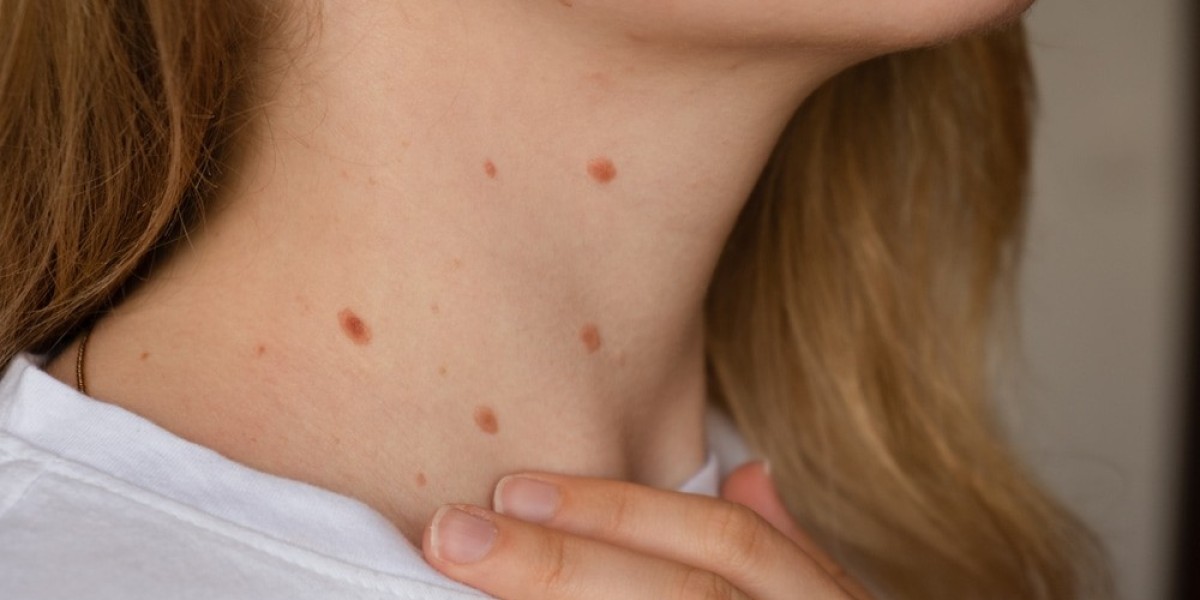
Skin tags, medically known as acrochordons, are small, fleshy growths that often form on the neck, armpits, eyelids, groin, and under the breasts. They are usually skin-colored or slightly darker and are painless unless irritated by clothing or jewelry. Although harmless, their appearance can be bothersome for cosmetic reasons.
Many people mistakenly believe that skin tags are caused by infections or viruses. Understanding their origin is crucial in answering the question: Are Skin Tags Contagious? In reality, skin tags are primarily caused by friction, genetics, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions, rather than infectious agents.
Causes of Skin Tags
Several factors contribute to the formation of skin tags. These include:
Friction: Repeated rubbing of the skin against clothing, jewelry, or skin folds.
Genetics: A family history of skin tags can increase susceptibility.
Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy or hormonal imbalances can trigger growth.
Obesity: Overweight individuals may experience more skin folds, increasing friction.
Medical Conditions: Diabetes and metabolic syndromes are sometimes associated with higher skin tag occurrences.
It is essential to note that skin tags are not caused by contagious pathogens like bacteria or viruses. This understanding directly relates to the main question: Are Skin Tags Contagious? Scientific evidence shows that you cannot "catch" a skin tag from another person.
Are Skin Tags Contagious?
The short answer is no: skin tags are not contagious. Unlike warts or fungal infections, which can spread from person to person, skin tags develop due to internal or mechanical factors rather than infectious agents. They do not transmit through touch, sharing clothing, or using personal items like towels.
Despite this, some people may notice multiple skin tags forming simultaneously. This does not indicate contagion but is usually related to factors such as genetics, age, or underlying medical conditions. While it is natural to worry about spreading them to family members, there is no evidence supporting the transmission of skin tags between individuals.
Common Misconceptions About Skin Tag Spread
Many myths exist around skin tags, often leading to confusion and unnecessary concern. Some of the most common misconceptions include:
Skin tags are contagious like warts: This is false. Warts are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), which can spread, whereas skin tags are benign growths unrelated to viral infections.
Touching a skin tag can cause more to appear: Skin tags are not spread through contact, so this is a misconception.
Poor hygiene causes skin tags: Hygiene does not play a role; friction and genetics are the main factors.
Understanding these misconceptions is vital for reducing unnecessary anxiety about skin health. Emphasizing Health and wellness, maintaining a balanced lifestyle, and practicing good skincare routines can help reduce the risk of developing skin tags, but they won’t prevent them entirely since genetics play a significant role.
Risk Factors for Skin Tags
Certain groups of people are more prone to developing skin tags due to underlying risk factors:
Middle-aged and older adults: Skin elasticity decreases over time, increasing friction-prone areas.
Overweight individuals: More skin folds result in more friction and a higher likelihood of skin tag formation.
People with insulin resistance: Diabetes and metabolic syndromes are linked to an increased number of skin tags.
Pregnant women: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can trigger new skin tag growth.
While these risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing skin tags, they do not imply that skin tags are infectious. Knowing these factors can help individuals understand their skin better and seek early intervention if necessary.
Treatment Options for Skin Tags
Although skin tags are harmless, many people choose to remove them for cosmetic reasons or if they cause discomfort. Treatment options include:
Cryotherapy: Freezing the skin tag with liquid nitrogen.
Excision: Surgical removal using scissors or a scalpel.
Ligation: Tying off the skin tag at the base to cut off blood supply, causing it to fall off.
Over-the-counter treatments: Some creams and solutions claim to remove skin tags, but their effectiveness varies.
It is important to avoid attempting removal at home with sharp objects, as this can cause infection or scarring. Consulting a dermatologist is always the safest approach. While removal addresses appearance or irritation, it does not affect the non-contagious nature of skin tags.
Prevention and Skin Care Tips
Preventing skin tags entirely may not be possible due to genetic and hormonal factors, but you can reduce the likelihood of new growths through the following measures:
Maintain a healthy weight: Reducing friction from skin folds can help.
Wear loose-fitting clothing: Avoids constant rubbing on sensitive areas.
Monitor hormonal changes: Pregnancy and other hormonal shifts can increase risk.
Practice good skin hygiene: Keeping skin dry and clean can reduce irritation, though it won’t prevent skin tags entirely.
Incorporating these practices supports overall Health and wellness, ensuring that your skin remains healthy even if skin tags develop. Regular check-ups with a dermatologist can also help identify other skin conditions that may require attention.
When to See a Doctor
While skin tags are generally benign, there are times when medical consultation is recommended:
Rapid growth or color change: Could indicate other skin conditions.
Pain or bleeding: Might suggest irritation or secondary infection.
Multiple new skin tags: Could be linked to underlying health issues such as diabetes or hormonal disorders.
Dermatologists can confirm whether a growth is a skin tag or another skin condition and provide safe removal options. Importantly, seeing a doctor also reinforces that skin tags are not contagious, relieving unnecessary worry about spreading them to others.
Conclusion
Understanding skin tags and their causes is key to addressing concerns about transmission. Scientific evidence clearly indicates that skin tags are not contagious, and they cannot be passed from person to person through touch or shared items. Factors such as friction, genetics, and certain medical conditions play a more significant role in their formation.
Focusing on overall Health and wellness, maintaining a balanced lifestyle, and seeking professional guidance when necessary ensures both your skin’s health and peace of mind. While skin tags may be a cosmetic concern, they are harmless and non-infectious, making fears about spreading them unfounded.